When you hear the term "Supercomputer," you probably picture a massive server room, rows of black cabinets, and a cooling system loud enough to deafen you.
But in 2026, a supercomputer looks different. It looks like the NVIDIA DGX Spark.
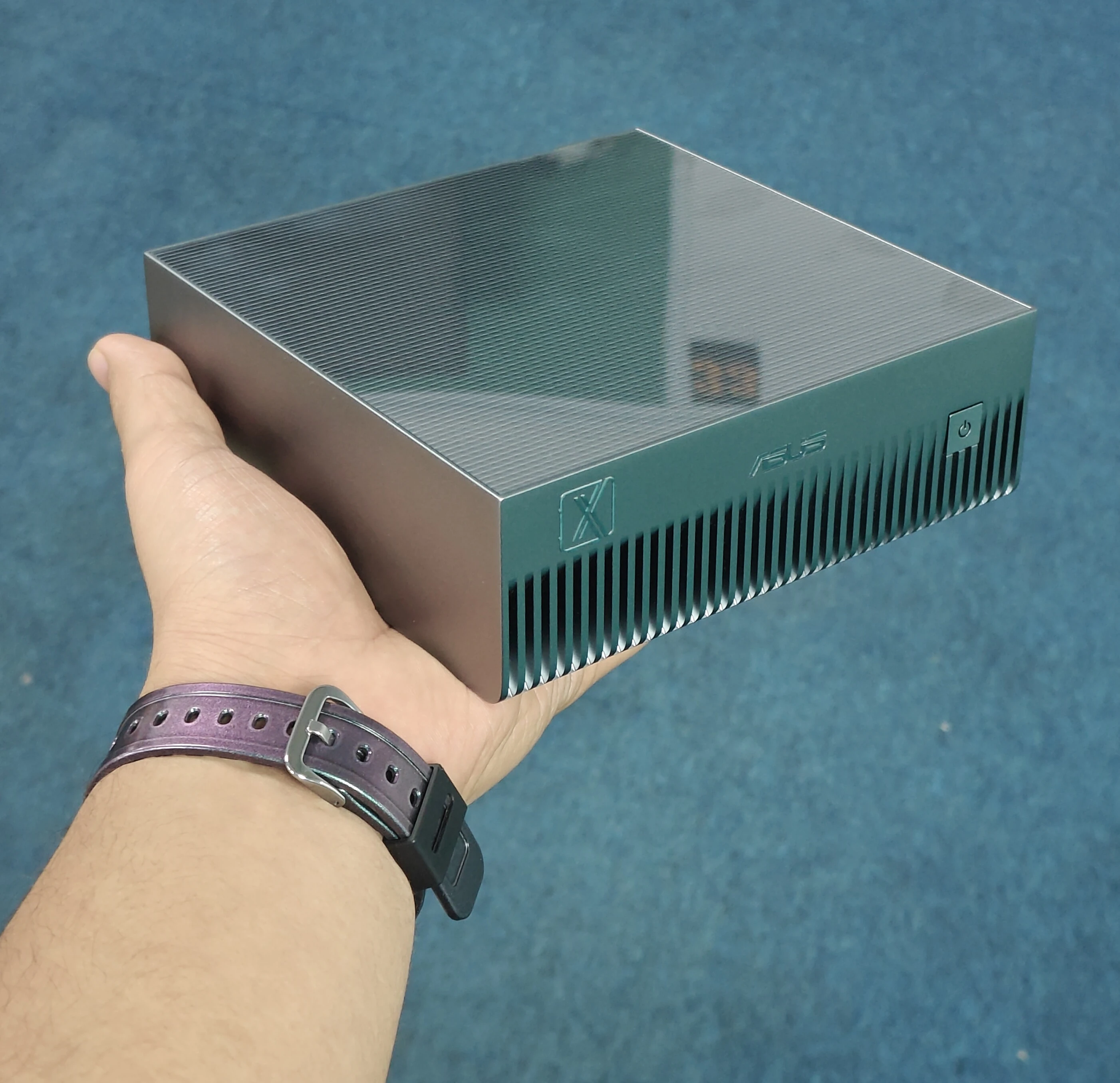
We tested the ASUS Ascent GX10 (a DGX Spark platform) against the best consumer GPU on the market, the RTX 5090.
The GB10 Architecture
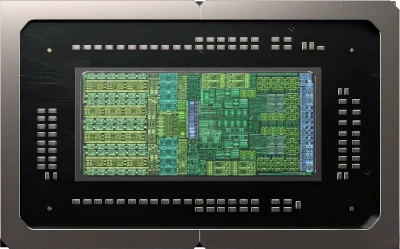
The reason this small device is called a "supercomputer" is the NVIDIA Grace Blackwell Superchip (GB10) inside.
In a traditional PC (like our 5090 test bench), you have a CPU on the motherboard and a GPU in a PCIe slot. They talk to each other over the PCIe bus a "single-lane highway".
The DGX Spark does it differently. It fuses a 20-core Arm CPU and a Blackwell GPU onto a single die. They are connected by NVLink-C2C (Chip-to-Chip), an internal connection moving data at 900 GB/s.
- Performance: This architecture delivers 1 PetaFlop of FP4 AI performance. It is heavily optimized for FP4 and INT4 quantization, allowing it to run massive models efficiently.
- Memory: It features 128GB of Unified LPDDR5X Memory. Unlike a standard PC where the CPU and GPU have separate RAM, here the entire 128GB pool is shared instantly. This allows you to load models up to 200 Billion parameters locally, something physically impossible on a 32GB RTX 5090.
Connectivity & Expansion
Despite its size, the I/O is built for pros:
- 4x 20Gbps USB Type-C ports (DisplayPort 2.1 compatible).
- One port supports 180W Power Delivery.
- 1x 10GbE LAN port.
- ConnectX-7 Port: This is the game-changer. It allows you to link two units together to double your performance and memory bandwidth. It effectively becomes a scalable cluster on your desk.
Real-World Testing
We tested the DGX Spark against an RTX 5090 workstation to see where it stands.
1. LLM Inference: The Capacity vs. Latency Trade-off
We tested a range of models from the nimble Qwen 2.5 to the massive Llama 3.2 90b.
Methodology Note: For the DGX Spark (GB10) tests, we split the benchmarks into "Generations" to stress-test the unified memory:
- Gen 1: A short, simple prompt (e.g., "Hi"). This tests immediate responsiveness.
- Gen 2 / Gen 3: Massive prompts with large context windows. This tests the system's ability to ingest and process huge amounts of data before generating a response.
[See AI Inference Benchmark Results Below]
5090
| LLM Model | VRAM Usage (Total) | Throughput (tokens/s) | Latency (ms/token) | Driver Version | CUDA Version | Total Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| llama3.1:latest | 6019.00 MB | 214.43 | 4.66 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 25849 |
| llama3.1:latest | 5970.00 MB | 218.44 | 4.58 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 26228 |
| deepseek-r1:70b | 30720.00 MB | 3.59 | 220.58 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 515 |
| deepseek-r1:70b | 30722.00 MB | 4.51 | 221.6 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 643 |
| deepseek-r1:1.5b | 2297.00 MB | 268.34 | 3.7 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 32472 |
| deepseek-r1:7b | 5657.00 MB | 191.54 | 5.19 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 23170 |
| deepseek-r1:8b | 6487.00 MB | 191.81 | 5.19 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 23106 |
| deepseek-r1:14b | 10759.00 MB | 122.01 | 8.19 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 14765 |
| deepseek-r1:32b | 20870.00 MB | 66.03 | 15.14 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 7970 |
| deepseek-r1:7b-qwen-distill-q4_K_M | 5657.00 MB | 198.2 | 5.02 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 23987 |
| gemma3n:e4b | 13082.00 MB | 83.14 | 12.02 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 10059 |
| gemma3:27b FP16 | 29309.00 MB | 0 | 0 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 0 |
| gemma3:27b | 29338.00 MB | 63.58 | 15.72 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 7641 |
| gemma3:8b-it-q4_K_M | 1821.00 MB | 180.99 | 6.18 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 19491 |
| gemma3:12b FP16 | 20043.00 MB | 56.56 | 17.65 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 6800 |
| qwen2.5:72b | 30706.00 MB | 0 | 0 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 0 |
| qwen2.5:latest | 30714.00 MB | 210.65 | 4.72 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 25491 |
| qwen2.5:0.5b | 1683.00 MB | 322.15 | 3.1 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 38743 |
| qwen2.5:0.5b | 1675.00 MB | 316.9 | 3.15 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 38094 |
| qwen2.5:1.5b | 370.0 MB | 53.35 | 18.74 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 6514 |
| qwen2.5:1.5b | 3608.00 MB | 312.38 | 3.18 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 37811 |
| qwen2.5:3b | 6479.00 MB | 274.54 | 3.64 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 32989 |
| qwen2.5:7b | 8522.00 MB | 221.23 | 4.51 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 26742 |
| qwen2.5:7b | 5653.00 MB | 223.69 | 4.46 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 27061 |
| qwen2.5:14b | 15532.00 MB | 135.84 | 7.35 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 16408 |
| qwen2.5:14b | 15532.00 MB | 150.29 | 6.64 | 560.76.05 | 12.6 | 18158 |
GB 10
| Model Name | Latency | Throughput (tok/s) |
|---|---|---|
| llama3.2-vision:90b (Gen 1) | 2273 ms | 4.4 |
| llama3.2-vision:90b (Gen 2) | 133319 ms | 4.62 |
| qwen2.5:72b (Gen 1) | 4359 ms | 2.29 |
| qwen2.5:72b (Gen 2) | 93051 ms | 4.62 |
| qwen2.5:72b (Gen 3) | 159590 ms | 4.58 |
| deepseek-r1:70b (Gen 1) | 35966 ms | 4.67 |
| deepseek-r1:70b (Gen 2) | 187090 ms | 4.68 |
| qwen2.5:32b (Gen 1) | 871 ms | 11.48 |
| qwen2.5:32b (Gen 2) | 12859 ms | 10.5 |
| qwen2.5:32b (Gen 3) | 11454 ms | 10.48 |
| deepseek-r1:32b (Gen 1) | 44044 ms | 10.4 |
| deepseek-r1:32b (Gen 2) | 31898 ms | 10.41 |
| gemma3:27b-it-fp16 (Gen 1) | 7518 ms | 4.66 |
| gemma3:27b-it-fp16 (Gen 2) | 211922 ms | 4.51 |
| gemma3:27b (Gen 1) | 2756 ms | 12.34 |
| gemma3:27b (Gen 2) | 26419 ms | 12.07 |
| gpt-oss:20b (Gen 1) | 2723 ms | 60.22 |
| gpt-oss:20b (Gen 2) | 22319 ms | 60.49 |
| deepseek-r1:14b (Gen 1) | 6584 ms | 24.76 |
| deepseek-r1:14b (Gen 2) | 20301 ms | 24.53 |
| qwen2.5:14b (Gen 1) | 384 ms | 26.02 |
| qwen2.5:14b (Gen 2) | 2496 ms | 24.44 |
| deepseek-r1:8b (Gen 1) | 4125 ms | 41.94 |
| deepseek-r1:8b (Gen 2) | 17316 ms | 42.16 |
| deepseek-r1:7b-qwen-distill-q4_K_M (Gen 1) | 11472 ms | 46.63 |
| deepseek-r1:7b-qwen-distill-q4_K_M (Gen 2) | 8232 ms | 46.65 |
| deepseek-r1:7b-qwen-distill-q4_K_M (Gen 3) | 22318 ms | 46.33 |
| qwen2.5:7b (Gen 1) | 200 ms | 49.9 |
| qwen2.5:7b (Gen 2) | 4769 ms | 46.97 |
| deepseek-r1:7b (Gen 1) | 4277 ms | 46.99 |
| deepseek-r1:7b (Gen 2) | 9220 ms | 46.86 |
| qwen2.5:3b (Gen 1) | 102 ms | 98.41 |
| qwen2.5:3b (Gen 2) | 647 ms | 102.06 |
| qwen2.5:3b (Gen 3) | 2899 ms | 100.74 |
| gemma3:1b-it-q4_K_M (Gen 1) | 52 ms | 190.68 |
| gemma3:1b-it-q4_K_M (Gen 2) | 3136 ms | 204.41 |
| qwen2.5:1.5b (Gen 1) | 62 ms | 160.9 |
| qwen2.5:1.5b (Gen 2) | 1504 ms | 186.83 |
| qwen2.5:1.5b (Gen 3) | 63 ms | 159.75 |
| qwen2.5:1.5b (Gen 4) | 707 ms | 188.13 |
| qwen2.5:1.5b (Gen 5) | 1445 ms | 186.15 |
| gemma3n:e4b (Gen 1) | 551 ms | 56.21 |
| gemma3n:e4b (Gen 2) | 6917 ms | 58.26 |
| qwen2.5:0.5b (Gen 1) | 25 ms | 404.23 |
| qwen2.5:0.5b (Gen 2) | 197 ms | 411.48 |
The Heavyweights (70B - 90B Models):
- Throughput: On Qwen 2.5 72B and Llama 3.2 90B, the GB10 maintained a steady 4.6 tokens/second.
5090 couldn't even load them. Its 32GB VRAM became bottleneck.
- Catch (Latency): Because the GB10 uses LPDDR5X memory (vs. the 5090's high-bandwidth GDDR7), the "Time to First Token" is high.
- On Llama 3.2 90B, we waited 133 seconds for the first word.
- On DeepSeek R1 70B, it took 180 seconds to start generating.
- On Llama 3.2 90B, we waited 133 seconds for the first word.
The Lightweights (Small Models):
- Qwen 2.5 7B: The 5090 is the clear winner here, delivering 220 tok/s with just 4.5ms latency. The GB10 managed 46 tok/s with a 22 second or 22,000ms latency.
- Gemma 1B Q4: Surprisingly, the GB10 outperformed the 5090 in throughput (204 tok/s vs. 160 tok/s), though the 5090 still won on latency (6ms vs. 3,000ms).
Why is the Latency So High? The "Gen 2" test involves feeding the AI a massive prompt (a large "context window"). The system has to read and process all that text before it can generate the first word of the answer. This is called the "Prefill" phase.
The RTX 5090 uses GDDR7 memory, which is incredibly fast (high bandwidth) but expensive and small (32GB). The DGX Spark uses LPDDR5X memory, which is massive (128GB) but has lower bandwidth.
Result: When the Spark has to ingest a huge book worth of text, it takes time to move that data through the LPDDR5X memory. You pay for the massive capacity with time. On the Spark, you wait 3 minutes, and then it starts working. On the 5090, you wait 0 seconds because the model crashes immediately on a model like DeepSeek R1 70B.
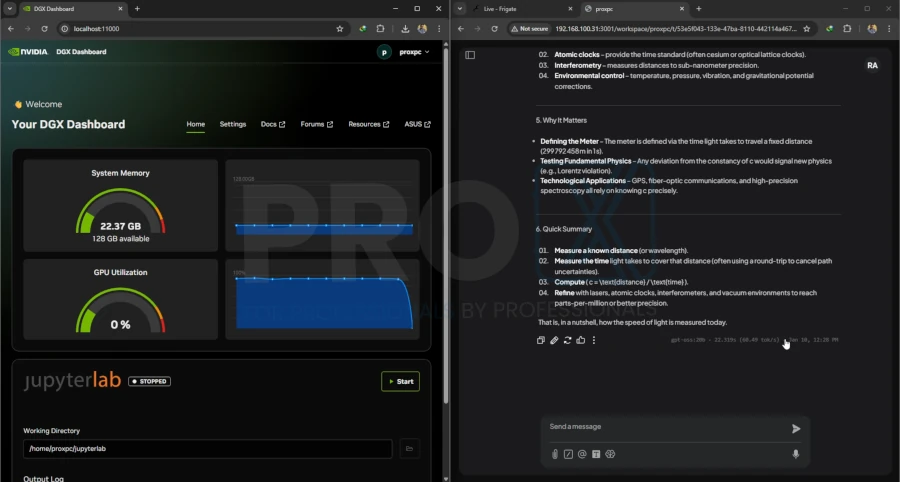
2. Fine-Tuning
[See Benchmark Results Below]
| Model | GPU | Training Time (Seconds) | Training Time (Minutes) | Peak Reserved Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20b GPT 0SS | 5090 | 207.1282 | 3.45 | 15.115 GB |
| 20b GPT 0SS | GB10 | 277.4285 | 4.62 | 19.354 GB |
| 120b GPT 0SS | 5090 | Failed | - | - |
| 120b GPT 0SS | GB10 | 1069.3322 | 17.82 | 59.158 GB |
Conclusion: If you need to fine-tune massive models locally, the Spark is your only option in it's price point.
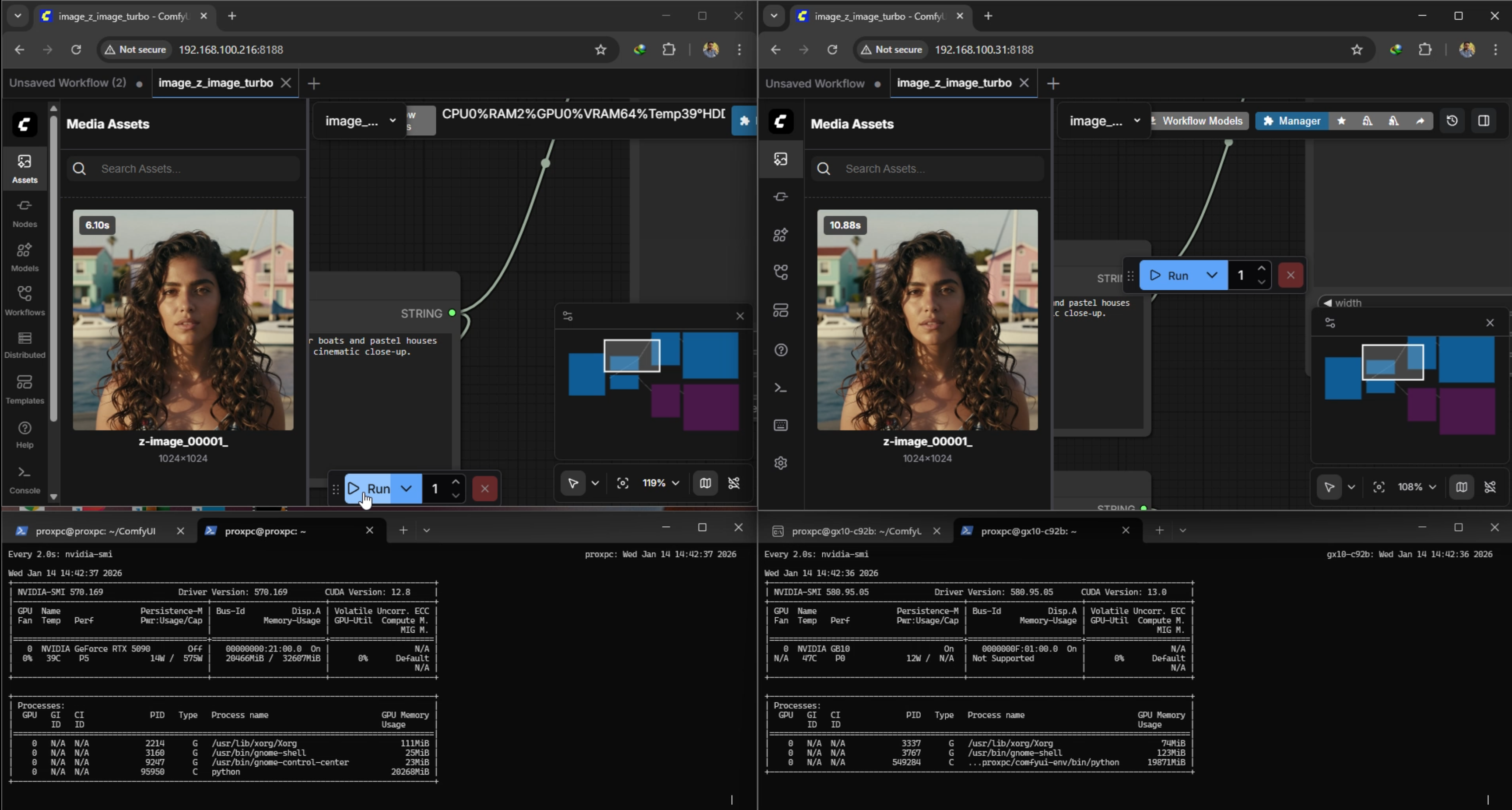
3. Creative Generation
[See Benchmark Results Below]
| Model / Workflow | Generation | RTX 5090 Time (s) | GB 10 Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| qwen3 4b + Image 2 turbo FP16 | Gen 1 | 6.1 | 10.8 |
| qwen3 4b + Image 2 turbo FP16 | Gen 2 | 1.69 | 6.17 |
| Flux Dev Mixed Precision | Gen 1 | 50 | 237 |
| Flux Dev Mixed Precision | Gen 2 | 56.6 | 156 |
| Flux Dev Mixed Precision | Gen 3 | 56.6 | 129 |
| Hunyuan Video 1.5 FP16 | Gen 1 | 1310 | 3606 |
Conclusion: For pure media creation, the RTX 5090's raw CUDA performance is superior. But if model is massive like GPT OSS 120B then 5090's raw power is of No use.
Power Usage
This was the most shocking part of our testing.
- RTX 5090 System: Drew roughly 800-900W from the wall (Card alone was 575W).
- DGX Spark (GB10): Completed all tests drawing under 100W.
You are getting PetaFlop-class AI performance for the power cost of a lightbulb.
Conclusion: Who is This For?
The DGX Spark isn't made for speed, and it’s not for training foundation models from scratch. It is for the Developer, the Student, and the Researcher who needs massive capacity in a tiny, silent, and efficient package.
It is about owning the compute.
With the DGX Spark, you can experiment, prototype, test, fine-tune, and run multiple or a huge AI models locally right at the corner of your desk, without a monthly cloud subscription.
Interested in the DGX Spark or the RTX 5090? We provide both solutions.
Email: sales@proxpc.com
Phone No.: 011-40727769